
Histology image of cardiac muscle*
[UPDATED] Cardiac muscle is one of the three types of muscle found in the human body. It is found exclusively in the heart, where it forms the main component of its middle layer, the myocardium.
[Myo]=combining form for "muscle"; [-card-]=heart; and [-ium]=layer or membrane. The myocardium is the muscle layer of the heart.
Cardiac muscle has distinct striations and intercalated discs (see accompanying image). The cardiac muscle acts as a functional syncytium.
The key characteristic of cardiac muscle is automatism or automaticity, its capacity to contract rhythmically in the absence of an external electrical stimulus. The other two types of muscle (smooth and skeletal) lack this characteristic.
The term [cardiomyocyte] can be used to describe each of these cells as the word is composed of [Card(i)o=combining form for "heart"; [myo]=combining form for "muscle"; and the suffix [-cyte]= cell. A cardiomyocyte is a cardiac muscle cell.
One of the components of the conduction system of the heart is made exclusively of cardiomyocytes.
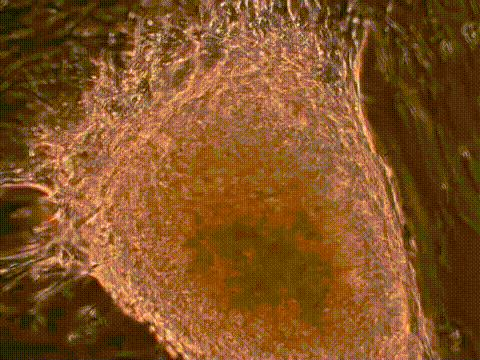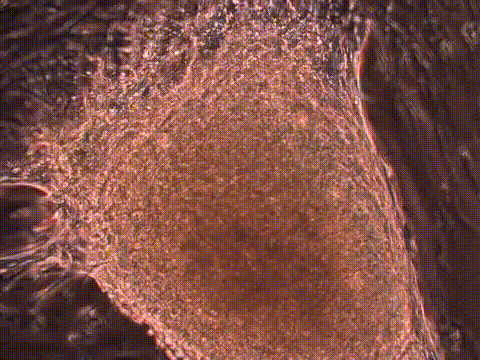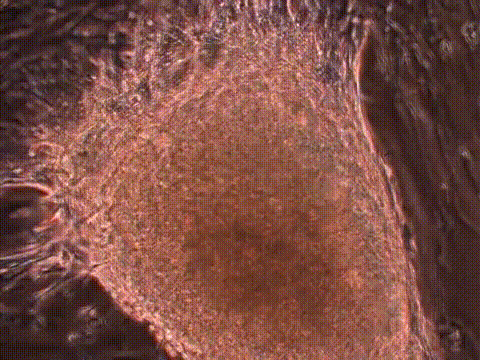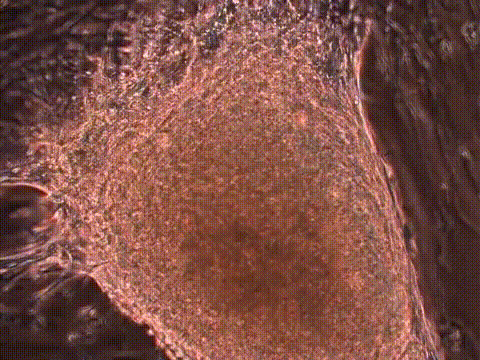
Image modified from the original on YouTube from the British Heart Foundation.
* Original histology image by S, Girod and A. Becker, courtesy of Wikipedia.