|
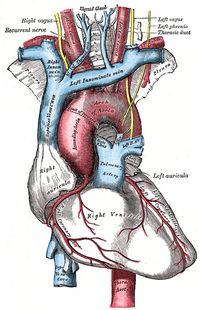
The pulmonary trunk is one of the great vessels of the heart. It is an artery that takes deoxygenated blood to the lungs as part of pulmonary circulation. It starts proximally at the pulmonary semilunar valve. This valve is situated at superior end of the outflow tract of the right ventricle, an area called the conus arteriosus. The pulmonary trunk has relation with the aorta on its right side, the left auricle and the left main coronary artery posteriorly. The pulmonary trunk is a short vessel, usually less than one centimeter in length. Most of the pulmonary trunk is found inside the pericardium. Almost immediately after it exits the pericardium it divides into a left and a right pulmonary artery, each one delivering deoxygenated blood to a lung. It is a common misconception to call this vessel the "pulmonary artery". This is not correct, as the pulmonary arteries are the left and the right pulmonary arteries. Sources: |
|
| Back to MTD Main Page | Subscribe to MTD |