|
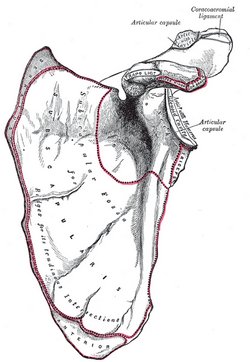
The [scapula] is a flat, triangular bone that forms the posterior portion of the shoulder girdle. It is described with two surfaces, three borders, and three angles. The scapula attaches to the clavicle by way of the acromioclavicular joint and ligaments. Seventeen muscles attach to the scapula providing stability and movement to the upper extremity.
The scapula has three well-defined borders. The medial border (vertebral border) is slightly convex. The superior border has a notch, the scapular notch, and a bony protuberance called the coronoid process. Where the superior and the lateral border (axillary border) meet there is a bony protuberance (the glenoid process) which has a shallow depression (the glenoid cavity), site of the glenohumeral joint or shoulder joint. Also, the lateral border presents with a small bony process just inferior to the glenoid process, the infraglenoid tubercle.
The scapula has two well-defined angles, the inferior and the superior angle, while the lateral angle is less defined because of the presence of the glenoid process.
The surfaces or the scapula are the anterior and posterior surface. The anterior or costal surface is slightly concave, fairly smooth with some oblique ridges. Being concave, this area is known as the subscapular fossa. The posterior surface is separated in two by an oblique bony process call the spine of the scapula. The scapular spine ends superolaterally in a bony process called the acromion. Also, the spine of the scapula divides the posterior surface of the scapula into a supraspinous fossa and an infraspinous fossa.
|
Anterior view of the left scapula. Image in Public Domain, by Henry Vandyke Carter - Gray's Anatomy |