|
UPDATED: The term [artery] evolved from two Greek words. The first one is [αέρα], meaning "air", and the second one is [terein], a verb meaning "to keep" or "to maintain"1. [Artery] therefore means "to maintain or to keep air", which is furthest from what we know today! The reason is that initial observations on these structures happened in bodies after combat, or gladiators who had exsanguinated because of their wounds. The arteries were empty (full of air) or contained a mix of blood and air. Arteries were considered a type of windipe. In fact, the original anatomical term for trachea was that of [tracheartery], which means "the rough artery". We have learned since then the true function of the arteries, so the name was shortened to "trachea".
The modern definition of an artery is "a structure that takes blood away from the heart". The amount of oxygen within the vessel has no bearing on the definition; there are arteries that carry oxygenated blood and arteries that carry deoxygenated blood.
|
|
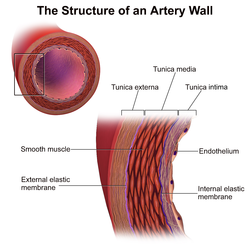
| Histologically, an artery is composed of three layers. The external layer is called the "adventitia" or "tunica externa". It is composed mostly of connective tissue. The middle layer is called the "tunica media" and is composed by a varying number of elastic fibers and smooth muscle fibers arranged as shown in the image. The inner layer is called the "tunica intima". The inner portion of the tunica intima is called the endothelium.
Arteries that are closer to the heart have more elastic fibers in their tunica media. As we move further away from the heart arteries become smaller and increase the number of smooth muscle fibers. This is what histologists describe "elastic arteries" and "muscular arteries". The smallest muscular arteries are called "arterioles". Large arteries have their own blood supply, called the "vasa vasorum".
Sources:
1. "The ancient Hellenic and Hippocratic origins of head and brain terminology" Panourias IG, Stranjalis G, Stavrinou L, Sakas DE. Clin Anat 2012 Jul;25(5):548-581
2. Image: "Blausen Gallery 2014" - Wikiversity Journal of Medicine. DOI:10.15347/wjm/2014.010. ISSN 20018762. Licensed under Creative Commons Attribution 3.0 via Wikimedia Commons - Original image
|