|
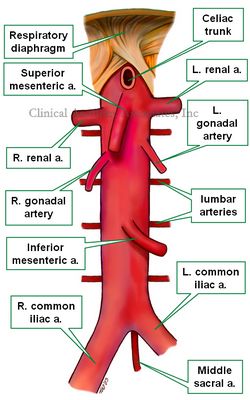
UPDATED: The abdominal aorta is the fourth, last, and most distal portion of the aorta. It begins when the descending aorta passes through the aortic hiatus of the respiratory diaphragm, just about the level of the 11th or 12th thoracic vertebra. It ends inferiorly at the bifurcation of the aorta, anterior to the lower portion of the body of the 4th lumbar vertebra where the abdominal aorta is continuous with the right and left common iliac arteries.
The abdominal aorta gives off a number of paired (bilateral) and unpaired (single) arterial branches. The paired branches are:
• Inferior phrenic arteries: provide blood supply to the respiratory diaphragm
• Renal arteries: Provide blood supply to the kidneys
• Gonadal arteries: Depending on the gender, they are called testicular or ovarian arteries, providing blood supply to the gonads
• Lumbar arteries: There are four pairs of lumbar arteries, which pass posteriorly around the vertebral bodies and provide supply to the spine and the back.
• Suprarenal arteries: These are several minute arteries that provide blood supply to the suprarenal glands. The suprarenal (adrenal) glands also receive several minute arteries that arise from the renal arteries and the inferior phrenic arteries.
The unpaired arterial branches of the abdominal aorta are:
• Celiac trunk: Provides blood supply to the stomach, spleen, liver, and duodenum
• Superior mesenteric artery: Provides blood supply to duodenum, jejunum, ileum, and the right side of the colon
• Inferior mesenteric artery: Provides blood supply to the left side of the colon, and superior aspect of the rectum
• Middle sacral artery: This is the only branch of the aorta that arises from its posterior aspect, it descends providing blood supply to the sacrum and fifth lumbar vertebra
|
Abdominal aorta- Anterior view. Click on the image for a larger version.
|
| Clinically, the abdominal aorta is divided by the origin of the renal arteries into a suprarenal and an infrarenal segment. This division is important for the surgical treatment of abdominal aortic aneurysms (AAA). To see a AAA, click here.
The suprarenal segment is bound laterally by the crura of the respiratory diaphragm. and its inferior boundary is the superior aspect of the highest renal artery (usually the left renal artery). It has branches that are critical for the blood supply of most of the digestive tract, the celiac trunk and the superior mesenteric artery, plus the inferior phrenic arteries and the suprarenal arteries.
The infrarenal segment includes the renal arteries, the inferior mesenteric artery, gonadal arteries, lumbar arteries, and the middle sacral artery.
Image property of:CAA.Inc.. Artist:Victoria G. Ratcliffe
|