The word acetabulum is formed by the combination of the Latin root [acetum], meaning "vinegar", and the Latin suffix [-abulum] a diminutive of [abrum], meaning a "cup", "holder", or "receptacle". Thus formed, the word acetabulum means "a small vinegar cup".
Roman soldiers liked to drink their water mixed with a small quantity of vinegar, so as to reduce the sensation of thirst. This mix was called "Posca". An acetabulum was used to add specific quantities of vinegar to the water, so over time the acetabula (plural form of acetabulum) were considered measuring devices. It is said that they measured one cup, or 2 1/2 oz. of wine.
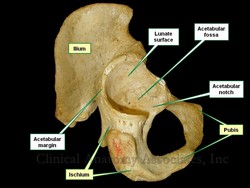
The anatomical acetabula are bilateral cup-like depressions in the os coxae which serve as a component of the coxofemoral joint (hip joint). They are found at the intersection of the three bony components of the os coxae, the ilium, ischium, and pubic bone and look anteroinferiorly.
The acetabulum has several components:
• Acetabular margin: An incomplete circular bony edge or border that marks the edge of the acetabulum
• Acetabular notch: The area where the acetabular margin is incomplete
• Acetabular labrum: Labrum (Lat. :lip). The acetabular labrum is a complete circular ring of fibrocartilage found on the acetabular margin that helps maintain the head of the femur in place. It is not shown in the accompanying image
• Lunate surface: A smooth, half-moon shaped area on the floor of the acetabulum. It is covered with hyaline cartilage and allows for articulation with the head of the femur
• Acetabular fossa: The non-articular region of the floor of the acetabulum. It contains fat, vessels, and the ligament of the head of the femur
Interesting fact: You may find that in older English anatomy books the acetabulum is referred to as the cotyloid cavity. The word cotyloid arises from the Greek [κοτυλοειδές] and means "similar to a cup". This separation in terms still exists when studying anatomy in other languages. For example, in Spanish the acetabulum is called "cavidad cotiloídea" or "cotilo", and in French it is called "cavité cotyloïde" or "cotyle". I guess the Greek soldiers did not drink vinegar with their water...
Image property of: CAA, Inc. Photographer: David M. Klein