This article is part of the series "A Moment in History" where we honor those who have contributed to the growth of medical knowledge in the areas of anatomy, medicine, surgery, and medical research.

Bernhard Siegfried Albinus
Bernhard Siegfried Albinus (1697-1770). German-Dutch physician, surgeon, and anatomist, Albinus was born in Frankfurt an der Oder, but lived most of his life in Leyden, in Holland, his adopted country. His real name was Bernhard Siegfried Weiss, which means “white” in German, the Latin version of which is “albus”, from where derives his Latinized name “Albinus”.
His father was also a physician, Bernard (or Bernhard) Weiss (1653 – 1721). He also took the last name Albinus, which makes following their history and genealogy a bit difficult.
Albinus moved to Leyden (Leiden) when he was only five years old, excelling at his studies and entering the University of Leyden at 12. He later moved to Paris, France to continue his studies on anatomy and surgery. He received his medical degree in 1719.
He began work at the University of Leyden as a Professor of Anatomy and Surgery, where he continued working until his death in 1770. He is considered one the most well-known anatomists of the 18th century.
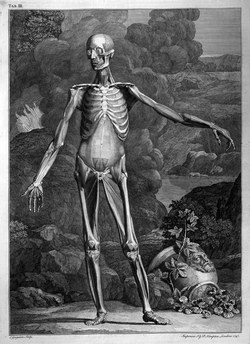
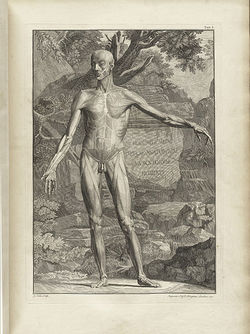
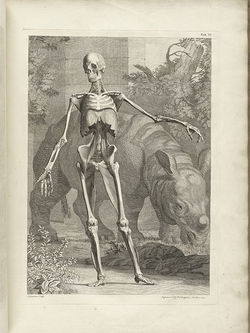
Because of his work with his colleague Herman Boerhaave (1668-1738), Albinus came in contact with Jan Wandelaar (1690-1759) an artist and engraver. It was this collaboration and the art of Jan Wandelaar which have made Albinus’ books and illustration famous. Albinus was criticized for the luscious, detailed, and sometimes strange backgrounds of his anatomical images, yet he defended Jan Wandelaar and his artistic expression. Albinus and Jan Wandelaar were dedicated to the faithful reproduction of anatomy in their publications, developing a grid system to reduce errors in production and printing.
During his tenure, Albinus was twice appointed Rector of the University and President of the College of Surgeons of Leyden. During this time, he became aware of the discovery of the copper plates created by Eustachius’ and lost for over a hundred years. In 1744 he published the plates in the book “Explanation of the Anatomical Tables of Eustachius “with his comments, stressing the fact that these images were better than those of Vesalius, published in 1543. This is no surprise, as Vesalius’ images were woodcuts, done before the technique of printing with copper plates became popular.
Although not well-known, Albinus’ name is eponymically attached to the risorius and scalenus minimus muscles. His famous publications include “Historia musculorum hominis” in 1734), “Icones ossium foetus humani” in 1737, “Tabulæ sceleti et musculorum corporis humani” in 1749, etc.
Some of Albinus and Jan Wandelaar images can be seen here. Click on the image to see a larger depiction:
Sources:
1. "Bernard Siegfried Albinus (1697-1770), German-Dutch anatomist" JAMA (1966), 196 (10): 910
2.“Bartholomeo Eustachio – The Third Man: Eustachius Published By Albinus” Fahrer, M. Ann Anat 187 (2005) 555—573
3. “Attic perfection in anatomy: Bernhard Siegfried Albinus (1697–1770) and Samuel Thomas Soemmerring (1755–1830)” Hildebrand, R. Ann Anat 187 (2005) 555—573
4. “Two Conceptions of the Human Form: Bernard Siegfried Albinus and Andreas Vesalius” Elkins, J. Artibus et Historiae, 7:14 (1986) 91-106
5. “Bartolomeo Eustachio: His Influence on Albinus and the Anatomical Models at La Specola, Florence” Hilloowala, R. J Hist Med All Sci (1986); 41 (4): 442 -462
Portrait and all other images in this article are in the public domain. Courtesy of Wikipedia. The links to read the books online courtesy of Archive.org.